Posterior Tibial Tendon dysfunction/ Adult Acquired Flat Foot Disorder.
The posterior tibial tendon connects the tibialis posterior muscle on the back of the lower legs to the bones in the centre of the sole of the foot. It is located deep behind the calf muscles.
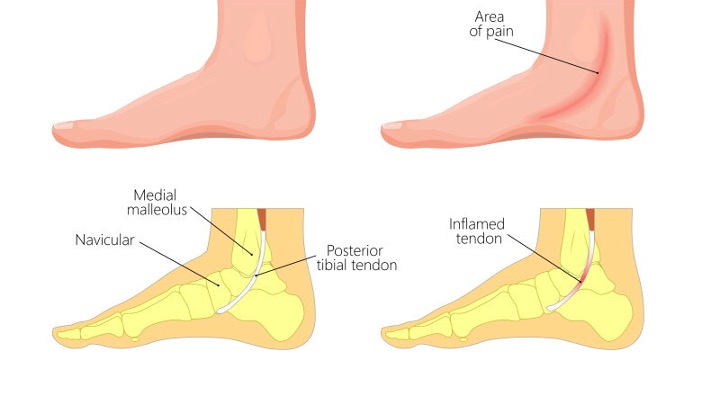
The tibialis posterior muscle is responsible for the downward and inward movement of the foot. The tendon helps to stabilise the structures at the bottom of your foot and your arch and lift the heel.
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) is a disabling condition caused by the loss of function of the tibialis posterior tendon.
What are the causes?
It is unknown what causes tibialis posterior dysfunction, but several factors have been linked to its development. Included are:
- Obesity
- Flat foot type
- Inflammatory joint diseases such rheumatoid arthritis, degenerative rupture.
- Previous surgery or trauma to the area.
- Excessive foot pronation
- Diabetes
- Hormonal imbalance
- Exposure to steroids, local steroid Injections to the area.
What part of the population is mostly affected?
It typically affects women between the ages of 40 and 60. Additionally, it is connected to prolonged standing, walking, and running. Approximately 2.3% to 3.6% of runners are affected by this condition.
The dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon is a common cause of Acquired Flatfoot deformity.
What are the signs and symptoms?
In the early stage, patients experience pain on the inside aspect of the ankle. There is no foot deformity at this stage but patients experience pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness as well as warmth along the tendon’s path.
The tendon may lengthen or rupture as the condition progresses. The foot flattens and becomes rigid. More tendon damage results from your foot flattening which causes complete tendon degeneration and a change in the angle of the ankle.
This loss of the height of the arch results in a deformity known as Adult Acquired Flat Foot Deformity. Typically, this transformation occurs on one leg. You will notice that the affected leg will lose strength and flexibility. This is extremely painful, so you will be unable to stand on your toes.
Early diagnosis and treatment are key to prevent progression of this problem and give patients a good outcome and if diagnosed in the later stages, PTTD requires surgical intervention.
This a problem that we diagnose and treat frequently in clinic. We use a combination of the following when treating patients with PTTD in clinic:
- Footwear changes
- Strapping and Taping
- Orthotics
- Laser
- Shockwave
- Exercise Rehabilitation
To find out more about treating and preventing Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction/ Adult Acquired Flat Foot Deformity download our guide Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
To contact us for more information on how we can help you, please complete the form below.
